Understanding Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Understanding Identity and Access Management (IAM)
The Growing Importance of IAM in Cybersecurity
A recent study by Verizon revealed that 63% of confirmed data breaches stem from weak, stolen, or default passwords. In cybersecurity, the saying goes, “No matter how good your chain is, it’s only as strong as your weakest link.” Hackers exploit these weak links—often through phishing attacks—to infiltrate organizations. Once inside, they use stolen credentials to plant backdoors, install malware, or exfiltrate confidential data, leading to severe consequences for businesses.
How Identity and Access Management (IAM) Works
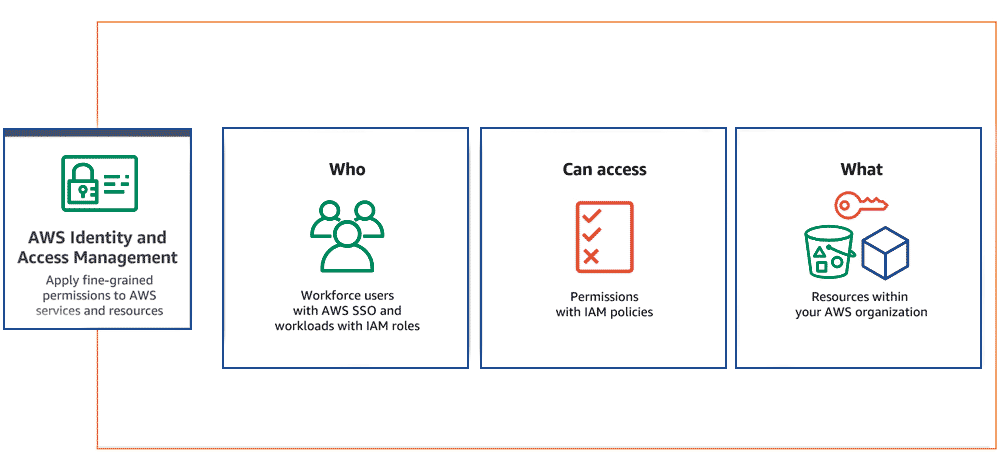
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides fine-grained permissions to manage access to AWS accounts and services. IAM enables organizations to control permissions at both an individual and group level, allowing roles to dictate access to critical resources.
What Is Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a combination of policies and technologies that help organizations identify users and grant appropriate access. With the rapid rise of cloud-based applications, controlling access to sensitive resources has become more challenging. IAM ensures secure, role-based access control while maintaining compliance with security standards.
IAM does not provide data replication or backup but plays a critical role in managing permissions for AWS resources. With IAM policies, organizations can enforce least-privilege access, ensuring users and systems only have access to what they need.
Key Components of IAM
Users – Individuals with authorized access to an organization’s systems.
Roles – Predefined sets of permissions assigned to users.
Groups – Collections of users with similar access requirements.
Policies – Rules that define user access to resources.
Benefits of IAM Systems
Enhanced Security: IAM prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems, thus minimizing the access of the unauthorized personnel.
Improved Compliance: It also guarantees that the organization complies with the legal requirements concerning the access control as well as the tracking of activities performed by the users.
Increased Productivity: Automates processes of the management of users and access, thus minimizing the numbers of manual operations and providing faster access to the required resources.
Reduced Risk: Portfolios reduce internal risks and data losses due to strict access protocols in place.
Centralized management is capable of consolidating identity and company access control and enforcing the same across different systems.
Importance of IAM for Organizations
1. Security
IAM ensures that only authorized individuals can access critical systems, mitigating risks from both internal and external threats.
2. Regulatory Compliance
IAM helps organizations adhere to industry regulations and legal requirements by tracking user activities and enforcing access controls.
3. Operational Efficiency
By automating tasks such as user onboarding, role changes, and offboarding, IAM reduces the burden on IT teams and enhances efficiency.
4. Risk Mitigation
IAM plays a vital role in preventing data breaches and cyberattacks by enforcing strict authentication measures.
5. Enhanced User Experience
IAM solutions improve accessibility for employees, partners, and customers while maintaining security.
IAM Technologies and Tools
Single Sign-On (SSO):
A choice that lets a user login and use multiple applications at once, as well as give more security to the services. Example: Its competitors include Okta and Microsoft Azure AD.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
A second one is that you must verify your account with two or more ways to boost its security. Example: Some of the examples of Two Factor Authentication applications are Duo Security and Google Authenticator.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
Secures the system based on employees’ roles, where the user will have the least privilege to access the system. Example: IBM Security Identity Manager.
Privileged Access Management (PAM):
Performs functions associated with obtaining and maintaining high levels of accessible (“privileged”) computing resources. Example: CyberArk, BeyondTrust.
Conclusion
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is an essential framework for ensuring that the right individuals access the right resources at the right time. By implementing IAM solutions, organizations enhance security, reduce unauthorized access risks, and comply with regulatory standards. As cyber threats continue to evolve, IAM remains a crucial component in safeguarding digital assets and ensuring seamless, secure user experiences. Organizations that adopt a strong IAM strategy will strengthen their cybersecurity posture and protect sensitive information effectively.
🚀 Ready to enhance security further? Explore additional AuthNull features to boost your enterprise authentication!