AuthNull Reimagining RADIUS Security for Modern networks.
Think of RADIUS as a Smart Security Guard for Computer Networks. Imagine you’re going to a high-security building. At the entrance, there’s a security guard who:
- Checks your ID (that’s authentication)
- Decides which rooms you can enter (that’s authorization)
- Keeps track of where you go and how long you stay (that’s accounting) RADIUS does exactly this, but for computer networks. It’s like a digital security system that makes and enforces rules about who can use the network and how they can use it.
Here’s how it works in everyday terms: When you try to connect to your office network or a Wi-Fi hotspot, RADIUS springs into action. It’s like having a smart doorman who:
- First checks if you are who you say you are (usually through your username and password)
- Creates a set of personalized rules just for you, considering things like:
- Are you an employee or a guest?
- What time is it?
- Where are you connecting from?
- What kind of access do you need? For example: - If you’re a regular employee, RADIUS might give you access to your work files and the internet - If you’re a guest, it might only let you use the internet, and maybe only for a few hours - If you’re trying to connect at an unusual time or from a strange location, it might add extra security checks
Think of it like having a VIP pass at a concert. The pass not only lets you in but also determines:
- Which areas you can enter
- How long you can stay
- What services you can use
The really clever part is that RADIUS can change these rules on the fly. If the network gets too busy, or if there’s a security concern, it can adjust everyone’s access automatically - just like a security guard might change the rules if a building gets too crowded or if there’s an emergency.
All of this happens in the background, usually in a split second, making sure everyone on the network stays safe and gets the access they need, when they need it. It’s like having a super-efficient security system that knows exactly who should get what access, when, and how - all without making anyone wait in long lines or fill out complicated forms.
That’s RADIUS in a nutshell - a smart, automated security guard for computer networks that makes sure everyone gets exactly the right kind of access they need, while keeping the network safe and organized.
Understanding RADIUS Bridge: A Deep Dive into Modern Authentication
In today’s interconnected world, secure authentication is more crucial than ever. RADIUS Bridge represents a sophisticated approach to managing network access, combining traditional RADIUS authentication with modern multi-factor authentication (MFA). Let’s explore how this system works and why it’s becoming increasingly important in enterprise environments.
What is RADIUS Bridge?
RADIUS Bridge is an authentication framework that connects multiple authentication systems:
- Network Policy Server (NPS)
- FreeRADIUS
- AuthNull (MFA service)
- Active Directory
It creates a seamless authentication flow while maintaining robust security through multiple validation layers.
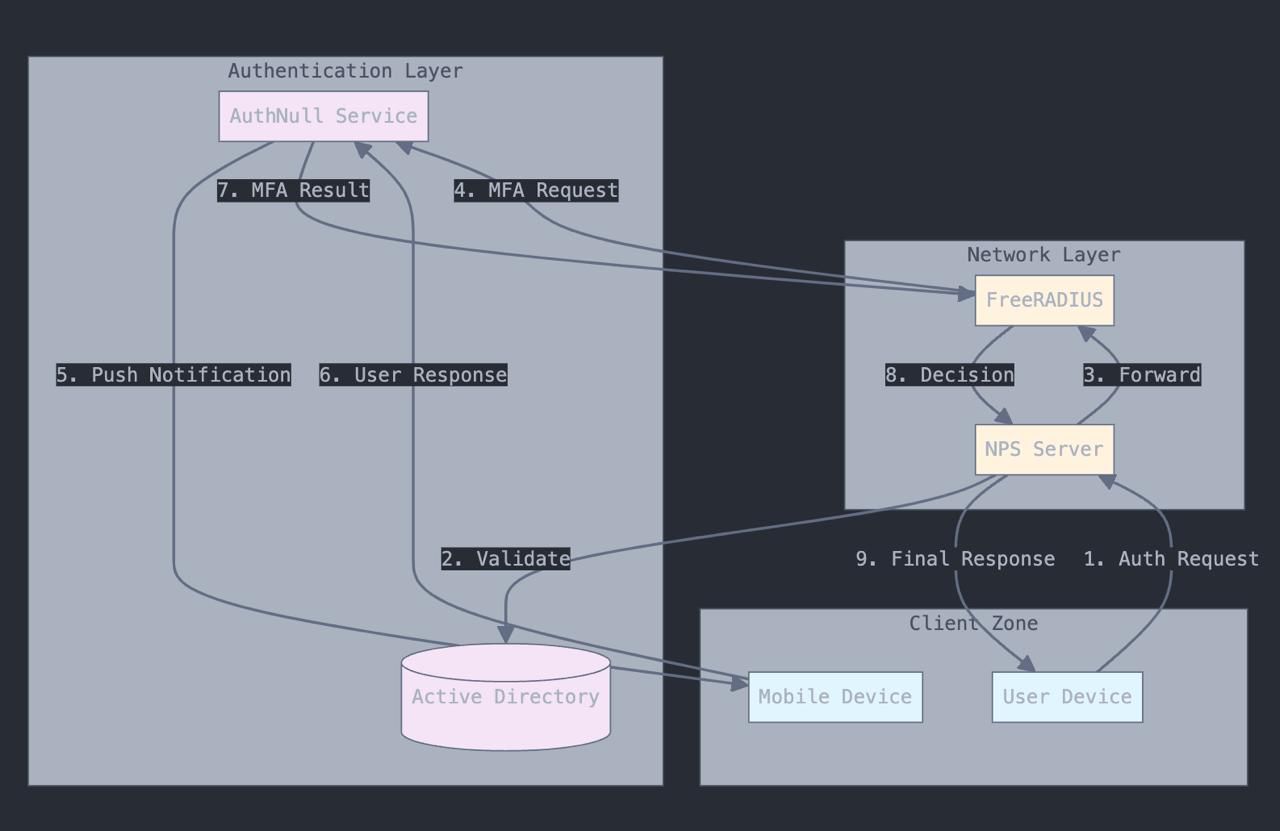
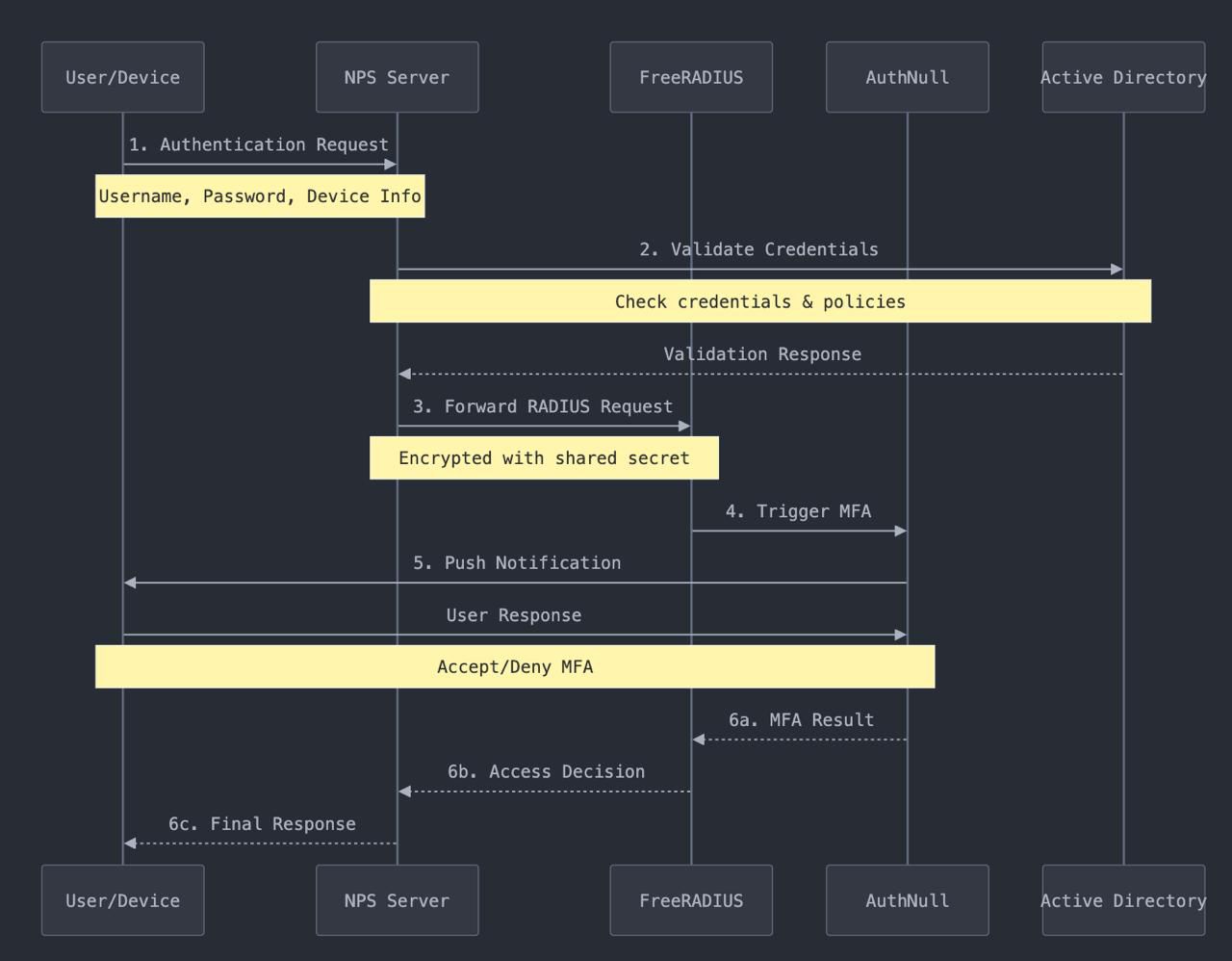
Authentication Flow Explained
1. Initial Request
When a user attempts to access network resources, their device sends an authentication request to the NPS server. This request includes:
- Username and password
- Device information
- Connection parameters
2. Active Directory Validation
The NPS server first validates the user’s credentials against Active Directory:
- Verifies username and password
- Checks group memberships
- Applies access policies
- Confirms account status
3. RADIUS Processing
Once AD validation is successful, NPS forwards the request to FreeRADIUS:
- Communication is encrypted using shared secrets
- Uses UDP ports 1812 (authentication) and 1813 (accounting)
- Includes relevant RADIUS attributes
4. Multi-Factor Authentication
FreeRADIUS initiates the MFA process through AuthNull:
- Triggers push notification to user’s mobile device
- Awaits user response
- Manages timeout scenarios
5. Final Authorization
The system completes the authentication chain:
- AuthNull returns MFA results
- FreeRADIUS makes final access decision
- NPS enforces the decision
- User receives access grant or denial
Security Measures
Communication Security
- RADIUS communications encrypted with shared secrets
- TLS for API calls
- Secure protocols across all channels
Authentication Security
- Multi-layer validation
- MFA integration
- Policy enforcement
- Real-time monitoring
Handling Failures
Network Issues
- Automatic retry mechanisms
- Connection timeout handling
- Failover protocols
Authentication Failures
- Account lockout policies
- Policy violation handling
- MFA timeout management
Timeout Settings
NPS Configuration
Authentication Timeout: 30 seconds Retry Attempts: 3 Retry Interval: 5 seconds
FreeRADIUS Configuration
Authentication Timeout: 30 seconds Response Wait: 30 seconds Maximum Retries: 3
Best Practices for Implementation
1. Regular Maintenance
- Rotate shared secrets
- Update security certificates
- Review access policies
2. Monitoring
- Set up comprehensive logging
- Configure alert systems
- Monitor performance metrics
3. Disaster Recovery
- Maintain backup configurations
- Test failover systems
- Document recovery procedures
Conclusion
RADIUS Bridge represents a modern approach to authentication, combining the reliability of RADIUS with the security of MFA. Its layered approach provides robust security while maintaining user-friendly access controls.
The system’s ability to handle failures gracefully, combined with its comprehensive security measures, makes it an excellent choice for organizations requiring secure, scalable authentication solutions.
Remember that successful implementation requires careful planning, regular maintenance, and continuous monitoring to ensure optimal performance and security.